
Metadataįinally, raster data should always be accompanied by metadata, which provides important information about the data, such as the date of acquisition, the spatial resolution, and the data source. This means that the data must be transformed from its original coordinate system to a common coordinate system that can be used with other data. Raster data must be projected in order to be used with other spatial data. For example, a satellite image may contain multiple bands that represent different wavelengths of light. Raster data can also contain multiple bands, with each band representing a different attribute of the geographic area. Each format has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the intended use of the data. Raster data can be stored in a variety of formats, including TIFF, JPEG, and GeoTIFF. Accuracy is determined by the quality of the data source and the processing methods used. While high spatial resolution data can provide more detail, it does not necessarily mean that the data is more accurate.
It’s important to note that spatial resolution does not always equal accuracy. However, interpolation can introduce errors and should be used with caution. Interpolation is commonly used in raster data to fill in gaps or create a smoother surface. Interpolation is the process of estimating values for locations where data is not available. This allows the data to be correctly located in space and used in conjunction with other spatial data. This means that each cell in the grid must be associated with a specific geographic location. Raster data must be spatially referenced in order to be used in GIS. Spatial referencing is another important characteristic of raster data. Binary data is used to represent presence or absence, such as in land cover classifications. Integer data represents whole numbers, while float data represents decimal numbers.

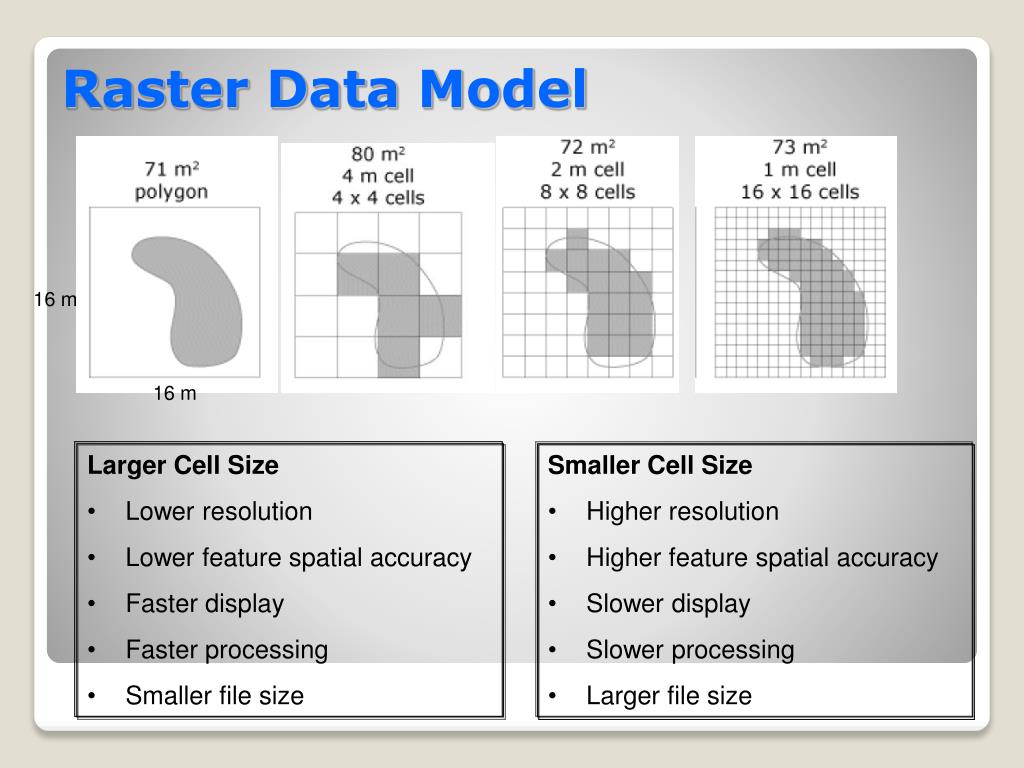
Raster data can come in a variety of data types, including integer, float, and binary. This can make working with raster data computationally intensive, as it requires a large amount of processing power and memory. Raster data can contain a large amount of data, especially if the spatial resolution is high. Data VolumeĪnother characteristic of raster data is its data volume. High spatial resolution data is useful for analyzing small areas or features, while low spatial resolution data is better for analyzing larger areas. The smaller the cell size, the higher the spatial resolution. Spatial resolution refers to the size of the cells in the grid. One of the most important characteristics of raster data is spatial resolution. Now that we know what raster data is, let’s explore the characteristics of raster data that make it unique and important in GIS. Difficult in a representation of Topology connections.Insufficient projection transformation.Loss of information when using large cells.Network analysis is difficult to perform.Dataset can be large, storage space can be a problem.A powerful format for statistical and spatial analysis.Each cell of a raster, stores a single value and it can be extended by using raster bands to represent RGB (red, green, blue) colors. In Raster, data is represented as a grid of (usually square) cells. Raster data can be images (raster images) with each pixel containing a color value. Raster data type consists of rows and columns of cells and these each cells stores a single value.
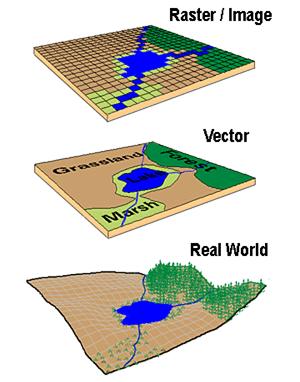
Digital Photography is the best example of raster data type model, anyone who is familiar with digital photography can recognize the pixels as the smallest individual unit of an image, where each pixel value in the image corresponds to a particular color and the combination of these pixels will create an image.Īs of now, the best example of raster data that is commonly used is Aerial photos, with only one purpose, to display a detailed image on a map or for the purposes of digitization. What are some applications of raster and vector data models?Ī raster data type is made up of pixel or cells and each pixel has an associated value.What is the difference between raster and vector data models?.FAQs: Understanding Raster and Vector Data Model In GIS.Raster vs Vector In GIS Comparison Chart:.Differences between Raster Data Model and Vector Data Model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
